"Type 2 Diabetes Syndrome Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines" recommends Bai Kangling® Zhenyuan Tablets for endocrine disorders (type 2 diabetes)
Release time:
2021-04-12 11:25
Source:
This guide mainly introduces the clinical application of the principle of combination of disease and syndrome, the basic process and operation method of diagnosis and treatment of diabetes, and mainly introduces the combination of disease and syndrome diagnosis, disease and syndrome treatment, and disease and syndrome rehabilitation. This guideline is mainly applicable to the attending physicians, resident physicians, regular training physicians and non-endocrinology clinicians engaged in clinical work at the front line, and is used in the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus using the principle of combination of disease and syndrome. The popularization and application of this guideline is of great significance for cultivating young doctors in my country to form the clinical thinking of active application of traditional Chinese medicine, to form the clinical habit of actively applying the principle of combination of disease and syndrome of traditional Chinese medicine to diagnose and treat diabetes, and to improve the level of TCM diagnosis and treatment of inpatients with diabetes in my country.
Professor Pang Guoming, deputy to the National People's Congress, an expert enjoying special government allowances from the State Council, chairman of Kaifeng Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and director of the National Regional Traditional Chinese Medicine (Endocrine) Diagnosis and Treatment Center, is the leader of the "Guide" expert group. Professor Pang Guoming introduced that the "Guide" was formulated and formulated based on clinical evidence and expert consensus opinions under the guidance of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association Branch of Integrative Medicine, and the Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Professional Committee organized the national front-line clinical experts in key specialties of TCM endocrinology. The guideline working group is composed of 19 expert teams from 18 provinces, 28 higher TCM colleges and scientific research institutions, a total of 62 people, and it lasted for 8 months. After repeated discussions, revisions and improvements, in early November Form a final draft. In order to ensure the authority of the standard, Professor Lin Lan of Guang'anmen Hospital of Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Professor Yang Shuyu, Director of Xiamen Diabetes Research Institute, Chairman of Diabetes Branch of Chinese Medicine Association, Professor Nan Zheng of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Professor Zhao Zhigang of Zhengzhou Yihe Hospital, Professor Qin Guijun of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Xia Weigang of Union Hospital are experts of the Steering Committee, and Shi Nannan, Lv Cheng, Peng Wei, Yang Tiansong and Xu Qiang are experts of the Methodology Expert Committee of the Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences.
The purpose of this guideline is to achieve "one liter and three drops", that is, to improve clinical efficacy, reduce morbidity, reduce fatality and disability rates, and reduce medical costs.
"Young and Middle-aged Experts with Outstanding Contributions" of the National Health Commission, Director of the Department of Endocrinology of Guang'anmen Hospital of the Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Director of the National Key Specialty "Traditional Chinese Medicine Endocrinology" of the National Health Commission and the State Administration of Central Administration Ni Qing, Affiliated to Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Chen Qiu, director of the hospital's major internal medicine department, director of the endocrinology department/diabetes center, and postdoctoral fellow of the Hallett Diabetes and Endocrinology Center of Brown University, respectively, introduced the guideline formulation online and interpreted the guideline.
Prof. Ni Qing made a report titled "Background of Diabetes Combination Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines".
https://v.qq.com/x/page/f320318j8nh.html
Professor Chen Qiu made an interpretation report entitled "Guidelines for Combining Diabetes and Diabetes with Type 2 Diabetes".
https://v.qq.com/x/page/x3203d9075w.html
Berkling® Vibration Film
Baikangling® Zhenyuan Tablet is a tablet extracted from the total saponins of ginseng fruit, which belongs to the traditional Chinese medicine medicine for nourishing qi and nourishing yin. The total saponins of ginseng fruit are the main active ingredients of Baikangling® Zhenyuan Tablets. Studies have shown that the total saponins of ginseng fruit mainly contain ginseng monomer saponins Rb1, Rb2, Rd, Rc, Re, Rg1 and so on.
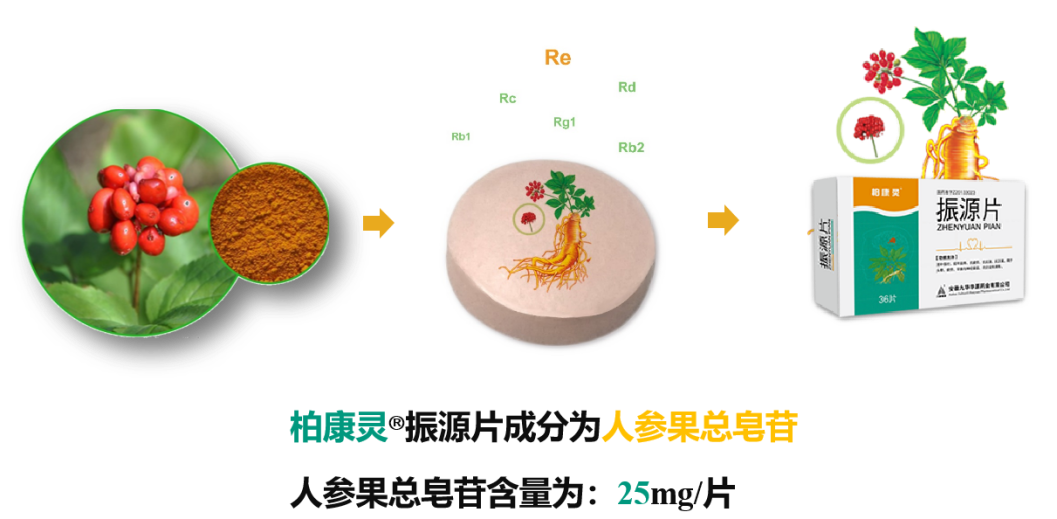
The potential of ginsenosides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and its complications
The effect of ginsenosides on type 2 diabetes is mainly to improve insulin resistance and improve insulin sensitivity. It is used to treat type 2 diabetes through multiple monomer saponin components acting on multiple targets, and for the treatment of diabetes and its complications, including type 2 diabetes, Diabetic cardiomyopathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic cognitive dysfunction, type 2 diabetes with fatty liver.
Study on the pharmacological effects of ginsenosides on type 2 diabetes and its complications
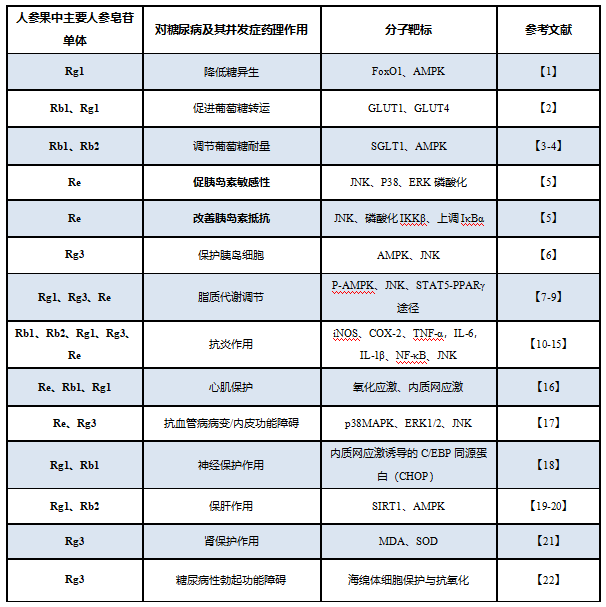
Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic syndrome characterized by long-term hyperglycemia. It is caused by the long-term interaction of genetic factors and environmental factors. Polyphagia, polyuria, weight loss, and fatigue are clinical manifestations of metabolic disorder syndrome, of which type 2 diabetes accounts for about 95%. Diabetes belongs to the category of diseases such as "diabetes disease" and "spleen deflation" in traditional Chinese medicine.
TCM syndrome differentiation standard
With reference to the Chinese Society of Integrative Medicine Endocrinology Professional Committee "Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Diabetes Diagnosis and Treatment Standards (Draft)", it is drawn up as early, middle and late stages.
early
The main clinical manifestations are dry mouth and polydipsia, heavy drowsiness, frequent urination, sticky stool or constipation, red tongue, yellow coating, and stringy pulse. The disease sites are mainly in the lungs, stomach, spleen and liver. The course of the disease is more than 5 years. There are no obvious complications. The main manifestations are hyperglycemia, obesity, relative insulin deficiency or insulin resistance. This period mainly includes the syndrome of excess heat and injury to the body fluid, the syndrome of liver stagnation and spleen deficiency, the syndrome of obstruction of phlegm and turbidity, and the syndrome of accumulation of dampness and heat.
medium term
The main clinical manifestations are mental fatigue and fatigue, shortness of breath and lazy speech, dry throat and mouth, polydipsia and desire to drink, red cheeks in the afternoon, short urination, dry stool, thin tongue, thin and dry coating, and a weak pulse. The main disease sites in this stage are the lungs, spleen, and kidneys. The course of the disease is usually 5 to 10 years. Combined with different degrees of microvascular complications. The main manifestations are insufficient insulin secretion and peak delay, which may be accompanied by insulin resistance. In this stage, there are mainly lung-kidney yin deficiency syndrome, spleen-spleen deficiency syndrome, and spleen-kidney qi deficiency syndrome.
late
The main clinical manifestations are frequent urination, dizziness and tinnitus, dry mouth and night, tetany, nocturnal emission, red tongue with little coating, thin pulse; , pale tongue with little fluid, weak and rapid pulse. The main disease sites in this stage are the liver, spleen and kidney. The course of the disease is more than 10 years. Macrovascular complications have occurred, and the condition is complicated. It is manifested as hypofunction of pancreatic β-cells and impaired viscera function. This period mainly includes liver and kidney yin deficiency syndrome and yin and yang deficiency syndrome.

【1】Liu, Q., Zhang, F. G., Zhang, W. S., Pan, A., Yang, Y. L., Liu, J. F., et al. (2017). Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits glucagon-induced hepatic gluconeogenesis through Akt-FoxO1 interaction. Theranostics 7, 4001–4012.
【2】Shang, W. B., Guo, C., Zhao, J., Yu, X. Z., and Zhang, H. (2014). Ginsenoside Rb1 upregulates expressions of GLUTs to promote glucose consumption in adiopcytes]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 39 , 4448–4452.
【3】Huang, Q., Wang, T., Yang, L., and Wang, H. Y. (2017b). Ginsenoside Rb2 alleviates hepatic lipid accumulation by restoring autophagy via induction of Sirt1 and activation of AMPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:1063.
【4】Song, B., Ding, L., Zhang, H., Chu, Y., Chang, Z., Yu, Y., et al. (2017). Ginsenoside Rb1 increases insulin sensitivity through suppressing 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type, I. Am. J. Transl. Res. 9, 1049–1057.
【5】Zhang Zhiguo. Study on the mechanism of ginsenoside Re in improving insulin resistance[D]. 2007.
【6】Kim, S. S., Jang, H. J., Oh, M. Y., Eom, D. W., Kang, K. S., Kim, Y. J., et al. (2014). Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances islet cell function and attenuates apoptosis in mouse islets. Transplant. Proceed 46, 1150–1155.
[7] Yao Peipei. Study on the mechanism of ginsenoside Re in improving lipid metabolism [D]. Qingdao University. 2014.
【8】Tian W, Chen L, Zhang L. Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on glucose metabolism and liver injury in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Genetics & Molecular Research Gmr, 16(1).
【9】Lee J B , Yoon S J , Lee S H , et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 ameliorated HFD-induced hepatic steatosis through downregulation of STAT5-PPARγ[J]. Journal of Endocrinology, 2017, 235(3):223-235.
【10】Huang, Q., Wang, T., and Wang, H. Y. (2017a). Ginsenoside Rb2 enhances the anti-inflammatory effect of omega-3 fatty acid in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by upregulating GPR120 expression. Acta Pharmacol . Sin. 38, 192–200.
【11】Wu, Y., Yu, Y., Szabo, A., Han, M., and Huang, X. F. (2014). Central inflammation and leptin resistance are attenuated by ginsenoside Rb1 treatment in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. PLoS ONE 9:e92618.
【12】Deng, J., Liu, Y., Duan, Z., Zhu, C., Hui, J., Mi, Y., et al. (2017). Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol-type saponins ameliorate glucose and lipid Metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus in high-fat diet/streptozocin-induced mice. Front. Pharmacol. 8:506.
【13】Kim, S. S., Jang, H. J., Oh, M. Y., Eom, D. W., Kang, K. S., Kim, Y. J., et al. (2014). Ginsenoside Rg3 enhances islet cell function and attenuates apoptosis in mouse islets. Transplant. Proceed 46, 1150–1155.
【14】Tian, W., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Wang, B., Li, X. B., Fan, K. R., et al. (2017). Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on glucose metabolism and liver injury in streptozotocin -induced type 2 diabetic rats. Gen. Mol. Res. 16:gmr16019463.
【15】Cho, W. C., Yip, T. T., Chung, W. S., Lee, S. K., Leung, A. W., Cheng, C. H., et al. (2006b). Altered expression of serum protein in ginsenoside re-treated diabetic rats detected by SELDI- TOF MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 108, 272–279.
【16】Yu, H. T., Zhen, J., Pang, B., Gu, J. N., and Wu, S. S. (2015). Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates oxidative stress and myocardial apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci . B. 16, 344–354.
【17】Shi, Y., Wan, X., Shao, N., Ye, R., Zhang, N., and Zhang, Y. (2016). Protective and antiangiopathy effects of ginsenoside Re against diabetes mellitus via the activation of p38 MAPK, ERK1/2 and JNK signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 14, 4849–4856.
【18】Liu, D., Zhang, H., Gu, W., Liu, Y., and Zhang, M. (2014). Ginsenoside Rb1 protects hippocampal neurons from high glucose-induced neurotoxicity by inhibiting GSK3β-mediated CHOP induction . Mol. Med. Rep. 9, 1434.
【19】Huang, Q., Wang, T., Yang, L., and Wang, H. Y. (2017b). Ginsenoside Rb2 alleviates hepatic lipid accumulation by restoring autophagy via induction of Sirt1 and activation of AMPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18:1063.
【20】Tian, W., Chen, L., Zhang, L., Wang, B., Li, X. B., Fan, K. R., et al. (2017). Effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on glucose metabolism and liver injury in streptozotocin -induced type 2 diabetic rats. Gen. Mol. Res. 16
【21】Kang, K. S., Ham, J., Kim, Y. J., Park, J. H., Cho, E. J., and Yamabe, N. (2013). Heat_x0002_processed Panax ginseng and diabetic renal damage: active components and action mechanism. J. Ginseng Res. 37, 379–388.
【22】Liu, T., Peng, Y. F., Jia, C., Yang, B. H., Tao, X., Li, J., et al. (2015b). Ginsenoside Rg3 improves erectile function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Sex. Med. 12, 611–620.
【23】Bai Litao, Gao Jialiang, Wei Fan. Therapeutic Potential of Ginsenosides as an Adjuvant Treatment for Diabetes[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9:423-437.
Related News

